


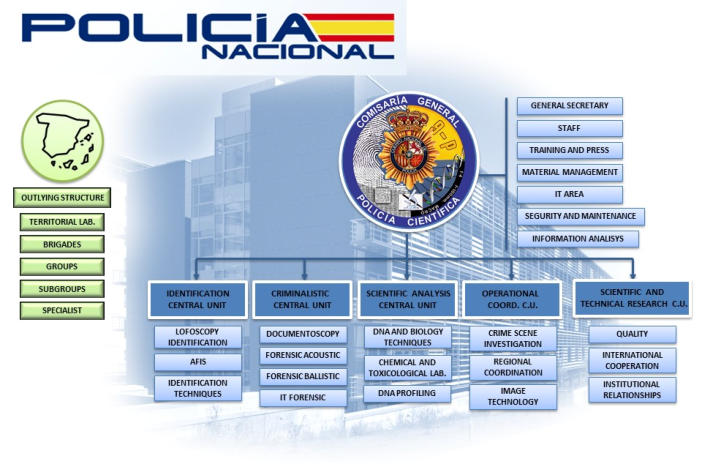
Scientific and Technical Research Central Unit
It assumes the functions related to scientific and technical research and quality control, as well as relations with other organizations and institutions, both national and international, in matters of forensic science. At present, three fundamental areas can be highlighted in its activity:Quality System:
Preparation of standardized procedures in all areas of Forensic Science, in accordance with internationally defined standards for the determination of the competence and technical validity of the Laboratory's activities (UNE EN ISO / IEC 17025: 2005) and for the operation of different types of organizations that carry out the inspection (UNE-EN ISO / IEC 17020: 2004). It is also the competent Unit for dialogue with the National Accreditation Entity (ENAC) which coordinates the participation of experts from the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police in activities related to quality in other forensic laboratories.International & Institutional Relations:
Responsible for coordinating the institutional activity, both National and International, of the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police with different organizations such as ENFSI, Interpol, Europol or AICEF (Ibero-American Academy of Criminal and Forensic Studies). Currently working on twinning projects with Turkey and Argelia and in a cooperation programme with SICA (SUBUD International Cultural Association).R + D + i
Promotion of research, development and innovation in collaboration with Universities and active participation in European projects.
UNITS





Operational Coordination Central Unit
Besides coordinating the regional groups is divided into two working areas:Crime Scene Investigation:
It carries out its work throughout the national territory regarding terrorism, fires, violent crime and organized crime. Participates with the Identification Techniques Section, in the identification of victims in Major Catastrophes.Image Technology:
It is responsible of making photographic reports in Ocular Inspections, the graphic capture of fingerprints and the immediate digital treatment process. Likewise, it performs the 3D reconstruction of crime scenes that are very useful for the Courts.Identification Central Unit
Divided into three different areas:Lofoscopy identification:
In charge of comparing the fingerprints revealed at the crime scene with those stored in the police database by making the corresponding expert's report. It is the national access point with Eurodac for asylum seekers.AFIS:
It facilitates the identification of the person under arrest and stores the lofoscopic evidence collected in the crime scene. Thus, they carry out the same functions of training specialists and maintain international relations within the framework of the Prüm Convention.Identification techniques:
It applies different techniques related to identifying the possible perpetrators of crimes such as face recognition and facial sketch, as well as bodies, dating the date of death through forensic entomology or regenerating the papillary crests. In charge of controlling the database of missing persons and unidentified bodies.Scientific Analysis Central Unit
Chemical & Toxicological Analysis:
Different work areas are framed, where we are able to analyze different material of different nature, such as fibres, pieces of glass, paintings, toxic substances , explosives, gunshot residues, fire accelerants,... with the aim of linking the author of a crime with its victim, or with the place, or with the objects of the crime.DNA analysis:
The DNA-Biology Laboratory- Mitochondrial DNA, nuclear DNA and Y chromosome, studies and analyses all types of evidence of biological origin, collected during the commission of criminal offences.Criminal Central Unit
It analyzes the items found in the crime scene and compares them with those stored in their corresponding databases in order to draw up the expert's report. It is divided into:Documentoscopy:
They carry out studies of forgery of documents, clothing, jewelry and works of art, as well as the handwriting analysis, including the terrorist field.Forensic Acoustics:
They analyze the sound and identify the perpetrator of a crime by their voice, or assist the Justice by establishing identity parades when the victim has not been able to see the perpetrator. It also makes a profile of the offender according to his language in what is called "voice passport" to help his location and subsequent arrest.Forensic Ballistics:
They analyze both the weapon and the ballistic elements in order to determine the type of weapon involved in a criminal act, their relationship and their involvement in other criminal offences. In the same way, they study the mechanics of the weapon and determine the bullet trajectory. Within this area, there is the Instrumental Traces department where they analyze and compare all kinds of marks found such as footprints, tires or those left by tools.IT Forensic:
Recovers and analyzes the information stored in all types of digital support, preserving its integrity through duplicating and blocking the alteration of the information under analysis.
INFORMATION

SPONSORS


Scientific and Technical
Research Central Unit
It assumes the functions related to scientific and technical research and quality control, as well as relations with other organizations and institutions, both national and international, in matters of forensic science. At present, three fundamental areas can be highlighted in its activity:Quality System:
Preparation of standardized procedures in all areas of Forensic Science, in accordance with internationally defined standards for the determination of the competence and technical validity of the Laboratory's activities (UNE EN ISO / IEC 17025: 2005) and for the operation of different types of organizations that carry out the inspection (UNE-EN ISO / IEC 17020: 2004). It is also the competent Unit for dialogue with the National Accreditation Entity (ENAC) which coordinates the participation of experts from the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police in activities related to quality in other forensic laboratories.International & Institutional
Relations:
Responsible for coordinating the institutional activity, both National and International, of the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police with different organizations such as ENFSI, Interpol, Europol or AICEF (Ibero- American Academy of Criminal and Forensic Studies). Currently working on twinning projects with Turkey and Argelia and in a cooperation programme with SICA (SUBUD International Cultural Association).R + D + i
Promotion of research, development and innovation in collaboration with Universities and active participation in European projects.





UNITS






Operational Coordination
Central Unit
Besides coordinating the regional groups is divided into two working areas:Crime Scene Investigation:
It carries out its work throughout the national territory regarding terrorism, fires, violent crime and organized crime. Participates with the Identification Techniques Section, in the identification of victims in Major Catastrophes.Image Technology:
It is responsible of making photographic reports in Ocular Inspections, the graphic capture of fingerprints and the immediate digital treatment process. Likewise, it performs the 3D reconstruction of crime scenes that are very useful for the Courts.Identification Central Unit
Divided into three different areas:Lofoscopy identification:
In charge of comparing the fingerprints revealed at the crime scene with those stored in the police database by making the corresponding expert's report. It is the national access point with Eurodac for asylum seekers.AFIS:
It facilitates the identification of the person under arrest and stores the lofoscopic evidence collected in the crime scene. Thus, they carry out the same functions of training specialists and maintain international relations within the framework of the Prüm Convention.Identification techniques:
It applies different techniques related to identifying the possible perpetrators of crimes such as face recognition and facial sketch, as well as bodies, dating the date of death through forensic entomology or regenerating the papillary crests. In charge of controlling the database of missing persons and unidentified bodies.Scientific Analysis Central Unit
Chemical & Toxicological Analysis:
Different work areas are framed, where we are able to analyze different material of different nature, such as fibres, pieces of glass, paintings, toxic substances , explosives, gunshot residues, fire accelerants,... with the aim of linking the author of a crime with its victim, or with the place, or with the objects of the crime.DNA analysis:
The DNA-Biology Laboratory- Mitochondrial DNA, nuclear DNA and Y chromosome, studies and analyses all types of evidence of biological origin, collected during the commission of criminal offences.Criminal Central Unit
It analyzes the items found in the crime scene and compares them with those stored in their corresponding databases in order to draw up the expert's report. It is divided into:Documentoscopy:
They carry out studies of forgery of documents, clothing, jewelry and works of art, as well as the handwriting analysis, including the terrorist field.Forensic Acoustics:
They analyze the sound and identify the perpetrator of a crime by their voice, or assist the Justice by establishing identity parades when the victim has not been able to see the perpetrator. It also makes a profile of the offender according to his language in what is called "voice passport" to help his location and subsequent arrest.Forensic Ballistics:
They analyze both the weapon and the ballistic elements in order to determine the type of weapon involved in a criminal act, their relationship and their involvement in other criminal offences. In the same way, they study the mechanics of the weapon and determine the bullet trajectory. Within this area, there is the Instrumental Traces department where they analyze and compare all kinds of marks found such as footprints, tires or those left by tools.IT Forensic:
Recovers and analyzes the information stored in all types of digital support, preserving its integrity through duplicating and blocking the alteration of the information under analysis.
INFORMATION

SPONSORS

Scientific and Technical Research
Central Unit
It assumes the functions related to scientific and technical research and quality control, as well as relations with other organizations and institutions, both national and international, in matters of forensic science. At present, three fundamental areas can be highlighted in its activity:Quality System:
Preparation of standardized procedures in all areas of Forensic Science, in accordance with internationally defined standards for the determination of the competence and technical validity of the Laboratory's activities (UNE EN ISO / IEC 17025: 2005) and for the operation of different types of organizations that carry out the inspection (UNE-EN ISO / IEC 17020: 2004). It is also the competent Unit for dialogue with the National Accreditation Entity (ENAC) which coordinates the participation of experts from the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police in activities related to quality in other forensic laboratories.International & Institutional Relations:
Responsible for coordinating the institutional activity, both National and International, of the General Headquarters of Forensic Science Police with different organizations such as ENFSI, Interpol, Europol or AICEF (Ibero-American Academy of Criminal and Forensic Studies). Currently working on twinning projects with Turkey and Argelia and in a cooperation programme with SICA (SUBUD International Cultural Association).R + D + i
Promotion of research, development and innovation in collaboration with Universities and active participation in European projects.
UNITS










Operational Coordination Central
Unit
Besides coordinating the regional groups is divided into two working areas:Crime Scene Investigation:
It carries out its work throughout the national territory regarding terrorism, fires, violent crime and organized crime. Participates with the Identification Techniques Section, in the identification of victims in Major Catastrophes.Image Technology:
It is responsible of making photographic reports in Ocular Inspections, the graphic capture of fingerprints and the immediate digital treatment process. Likewise, it performs the 3D reconstruction of crime scenes that are very useful for the Courts.Identification Central Unit
Divided into three different areas:Lofoscopy identification:
In charge of comparing the fingerprints revealed at the crime scene with those stored in the police database by making the corresponding expert's report. It is the national access point with Eurodac for asylum seekers.AFIS:
It facilitates the identification of the person under arrest and stores the lofoscopic evidence collected in the crime scene. Thus, they carry out the same functions of training specialists and maintain international relations within the framework of the Prüm Convention.Identification techniques:
It applies different techniques related to identifying the possible perpetrators of crimes such as face recognition and facial sketch, as well as bodies, dating the date of death through forensic entomology or regenerating the papillary crests. In charge of controlling the database of missing persons and unidentified bodies.Scientific Analysis Central Unit
Chemical & Toxicological Analysis:
Different work areas are framed, where we are able to analyze different material of different nature, such as fibres, pieces of glass, paintings, toxic substances , explosives, gunshot residues, fire accelerants,... with the aim of linking the author of a crime with its victim, or with the place, or with the objects of the crime.DNA analysis:
The DNA-Biology Laboratory- Mitochondrial DNA, nuclear DNA and Y chromosome, studies and analyses all types of evidence of biological origin, collected during the commission of criminal offences.Criminal Central Unit
It analyzes the items found in the crime scene and compares them with those stored in their corresponding databases in order to draw up the expert's report. It is divided into:Documentoscopy:
They carry out studies of forgery of documents, clothing, jewelry and works of art, as well as the handwriting analysis, including the terrorist field.Forensic Acoustics:
They analyze the sound and identify the perpetrator of a crime by their voice, or assist the Justice by establishing identity parades when the victim has not been able to see the perpetrator. It also makes a profile of the offender according to his language in what is called "voice passport" to help his location and subsequent arrest.Forensic Ballistics:
They analyze both the weapon and the ballistic elements in order to determine the type of weapon involved in a criminal act, their relationship and their involvement in other criminal offences. In the same way, they study the mechanics of the weapon and determine the bullet trajectory. Within this area, there is the Instrumental Traces department where they analyze and compare all kinds of marks found such as footprints, tires or those left by tools.IT Forensic:
Recovers and analyzes the information stored in all types of digital support, preserving its integrity through duplicating and blocking the alteration of the information under analysis.
INFORMATION

SPONSORS














